
Innovation
9 living labs for zero food and waste
9 innovative Living Labs
Systemic Innovations Towards a Zero Food Waste Supply Chain
- #1 FLW MONITORING AND ASSESSMENT >
- #2 SUSTAINABLE AND SMART PACKAGING >
- #3 WASTELESS GREENHOUSE SOLUTIONS >
- #4 MOBILE FOOD VALORISATION AS A SERVICE >
- #5 UGLY FOOD IDENTIFICATION >
- #6 DATA DRIVEN PRODUCTION PROCESS CONTROL >
- #7 EFFICIENT FOOD BANK NETWORKS >
- #8 FLW VALORISATION THROUGH ALGAE PRODUCTION >
- #9 INFORMING AND NUDGING CONSUMERS >
Factors affecting FLW
- Missing/fragmented FLW data (arduous/inaccurate data collection, largely based on subjective assessments and varied FLW definitions, not supporting effective reduction strategies);
- Limited food actor capabilities to reduce FLW especially in cases of diverse, seasonal & disruption-generated food surpluses or sub-standard products;
- Inability to steer consumer buying behaviour towards reducing FLW at the critical point that the purchase occurs;
- Understanding of packaging as an unavoidable secondary waste stream rather than a FLW-reducing opportunity;
- Unbalanced (unjust) allocation of FLW innovation cost/benefits among food chain actors.
Multitude of solutions to make a real impact to FLW
Data for FLW reduction
9 Living Labs
Systemic Innovation Living Labs
The methodology that ZeroW uses to coordinate our multi-organizational innovation process is the Living Lab approach.
It is focused on a systemic co-creation methodology that involves the full scope of food chain actors and beyond: introducing social and governance dimensions to industrial partners in a real-life setting.
ZeroW has built up 9 real-life Living Labs embedding systemic innovations with the potential to lead to fundamental changes in both social dimensions (values, regulations, attitudes) and technical dimensions (infrastructure, technology, tools, processes) and, most importantly, in the relations between them.
#1 FLW MONITORING AND ASSESSMENT >
#2 SUSTAINABLE AND SMART PACKAGING >
#3 WASTELESS GREENHOUSE SOLUTIONS >
#4 MOBILE FOOD VALORISATION AS A SERVICE >
#5 UGLY FOOD IDENTIFICATION >
#6 DATA DRIVEN PRODUCTION PROCESS CONTROL >
#7 EFFICIENT FOOD BANK NETWORKS >
#8 FLW VALORISATION THROUGH ALGAE PRODUCTION >
#9 INFORMING AND NUDGING CONSUMERS >
What will come out of the 9 Living Labs?
End products/services
.jpg&width=640&format=webp&quality=90)
Get more information
about the ZeroW project
A European project about systemic innovations for zero food waste.
More about ZeroWZeroW project
Work Package Objectives
Modelling FLW economics from F2F
WP1
- To outline a conceptual framework for measuring the economic effects of FWL along the food chain.
- To develop a high-level economic model encompassing the food supply chain actors and validate it by the Living Labs.
- To quantitatively assess various FLW interventions by running simulations with the FLW model.
0FLW
Data Space
WP2
- To establish semantic interoperability through a managed European 0FLW Data Space for the digital support needed for reducing FLW.
- To establish collaborative business and governance models for data sharing in 0FLW.
- To establish a federating catalogue to ensure interoperability between data sources.
- To support the SILLs in establishing interoperability, business models & governance.
- To develop an integrated kit to ‘onboard’ 0FLW initiatives, both from ZeroW and non-ZeroW partners, during and after the project.
Data-driven near-zero FLW Smart Applications
WP3
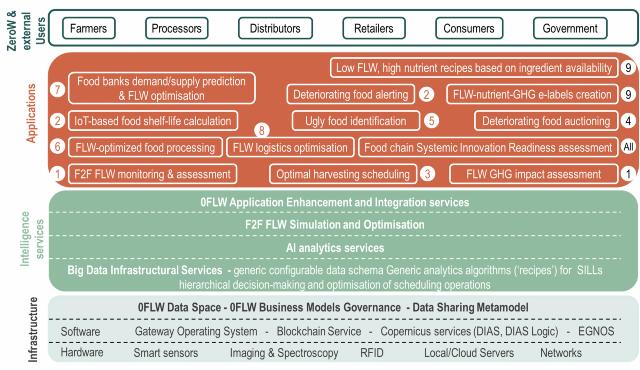
To provide a suite of Data-driven Intelligence Services (see figure) consisting of 4 key components:
- Big Data Infrastructural Services.
- 0FLW Application Enhancement and Integration Services in support of the SILLs solutions.
- AI Analytics and Visualization Services supporting key aspects of FLW management.
- SILL Actors Incentives Assessment and Optimisation Services.
Systemic Innovation management & demonstration
WP4
- To provide an enabling Living Lab environment for FLW Systemic Innovations to flourish.
- To manage the SILL communities and steer their activities from ideation to demonstration, through learning feedback cycles.
- To ensure a strong interaction between the SILLs and the impact assessment, scaling up, commercialisation and policy support activities of the project.
- To ensure an evolutionary process of the SILLs from a baseline to a higher level of systemic innovation readiness.
Systemic Innovation assessment
WP5
- To deliver a methodology for assessing FLW systemic innovations.
- To assess the SILL impacts, risks, sustainability trade-offs & level of 'just' allocation.
- To provide cluster-, place-, context- actor-, & gender-based consolidation & interpretation of results.
Fostering systemic innovation & building capacity
WP6
- To support the scaling up of the FLW systemic innovation solutions and approaches in EU regions with high potential.
- To organise capacity building activities for food actors & consumers aiming for increased value (economic, environmental, social) from FLW innovations.
- To build up regional specific upscaling strategies to stimulate investment in FLW reduction by private and public actors.
Exploitation, sustainability & commercialisation of project outputs
WP7
- To advance ZeroW’s innovative solutions commercially.
- To protect the commercially sensitive and strategic IP through 3 formal Patent filings; (3) to formulate a business- and market-relevant exploitation strategy with the end goal of self-sustaining revenues and a sustainable commercial trajectory; (4) to anchor the exploitation, business models, licencing models and go-to-market strategy through robust market sector analyses and commercial solution alignment imperatives.
Policy recommendations for just transition to near-zero FLW
WP8
- To provide alternative transition pathways towards near-zero FLW.
- To define a 'just' transition pathway to near-zero FLW and intermediate targets.
- To deliver short-, medium-term policy recommendations.
Cooperation with EC services & other
projects and/or initiatives
WP9
- To deliver an Action Plan for stakeholder & initiative engagement and cooperation with EC services.
- To establish collaborative ecosystems with relevant stakeholders in different frameworks.
- To engage with EU, National and global initiatives on a dialogue towards FLW policy, regulatory and commercialisation opportunities.
Visit ZeroW systemic innovation living labs









